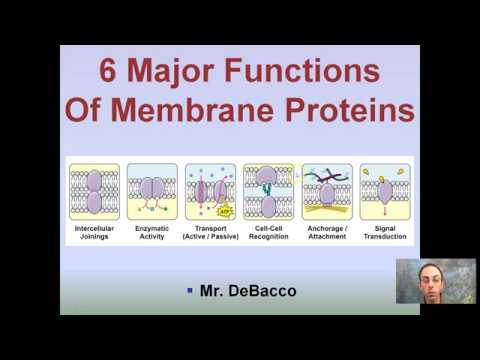
39 label the structure and functions of membrane proteins
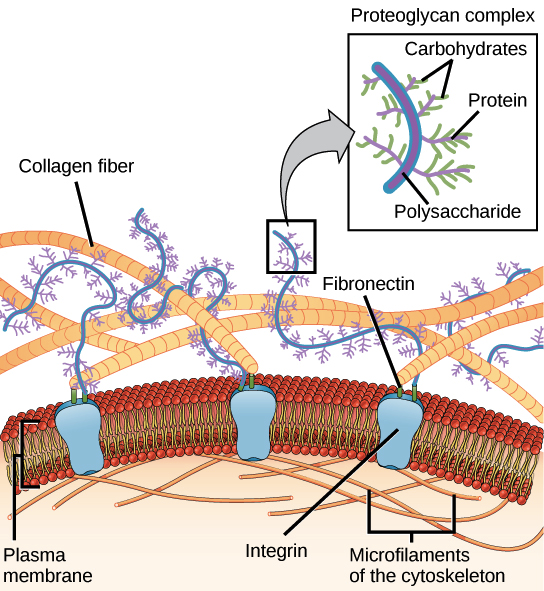
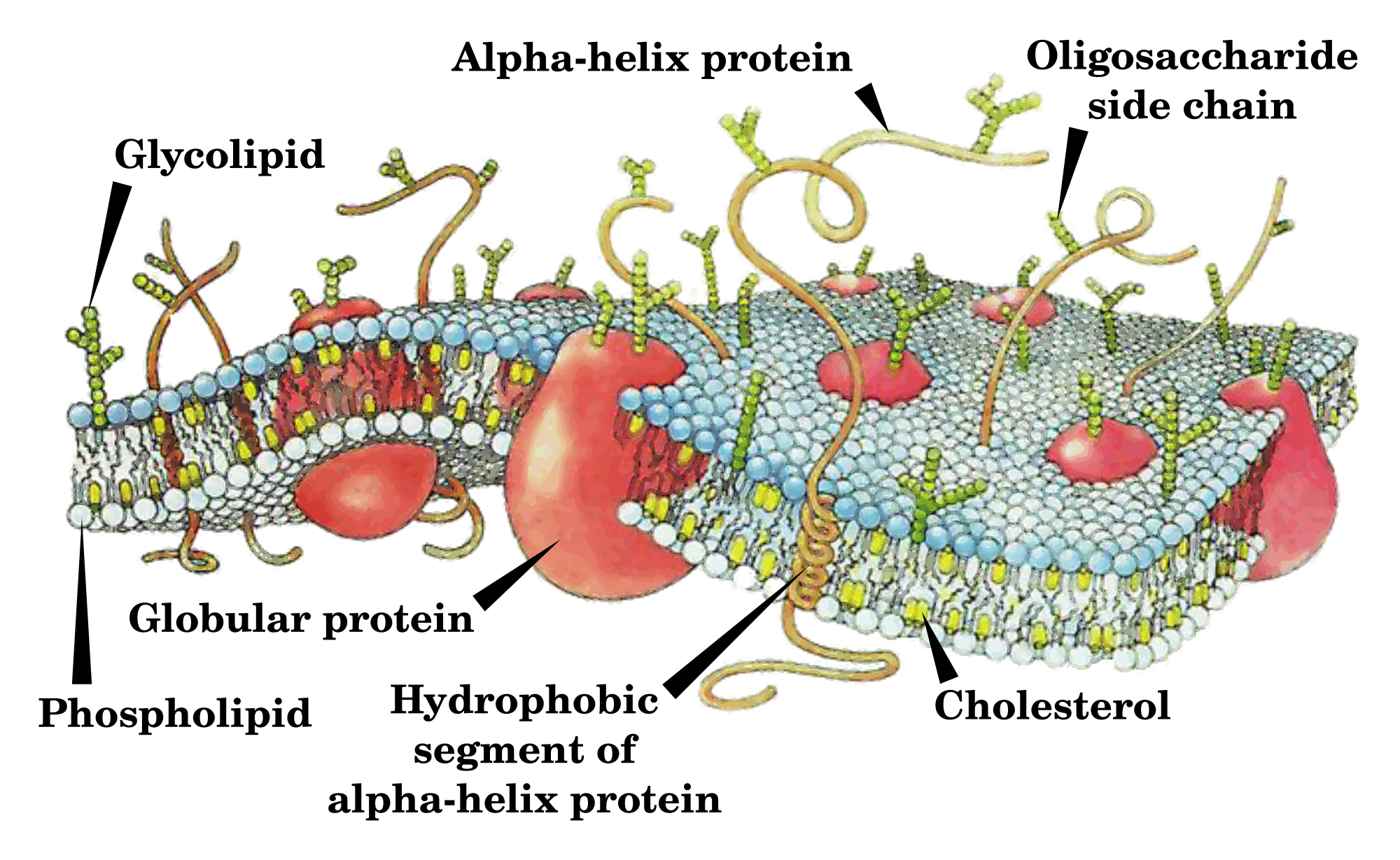
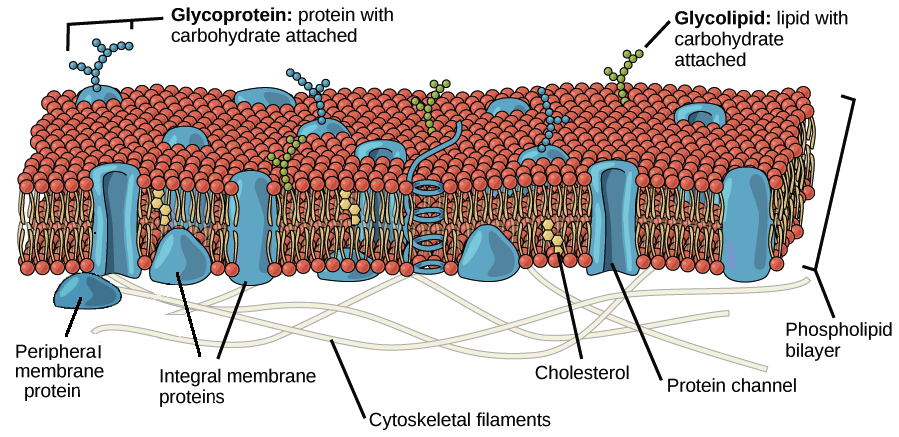
Structure determination of α-helical membrane proteins by solution ... This review summarizes the multiple strategies available for expression of isotopically labeled membrane proteins. Different environments for mimicking lipid bilayers will be presented, along with the most important NMR methods and labeling schemes used to generate high-quality NMR spectra. Membrane Structure & Function (Chapter 7) Flashcards - Quizlet -Membrane proteins can bond to the cytoskeleton or to molecules of the extracellular matrix. This helps maintain the shape of the cell and stabilizes the membrane proteins. -A glycoprotein is a membrane protein with an attached short branched carbohydrate chain.
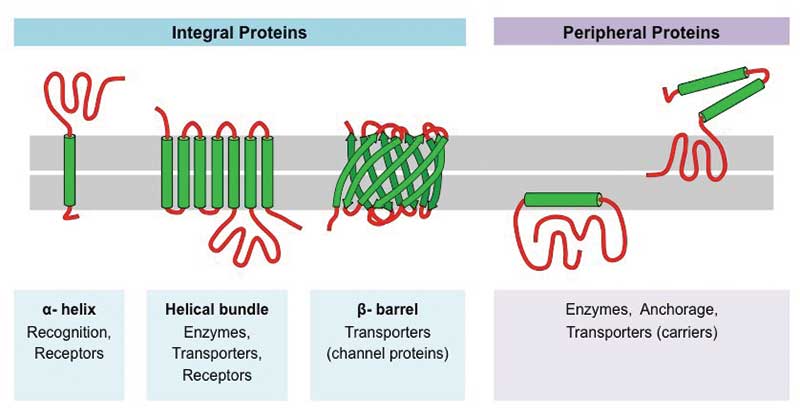
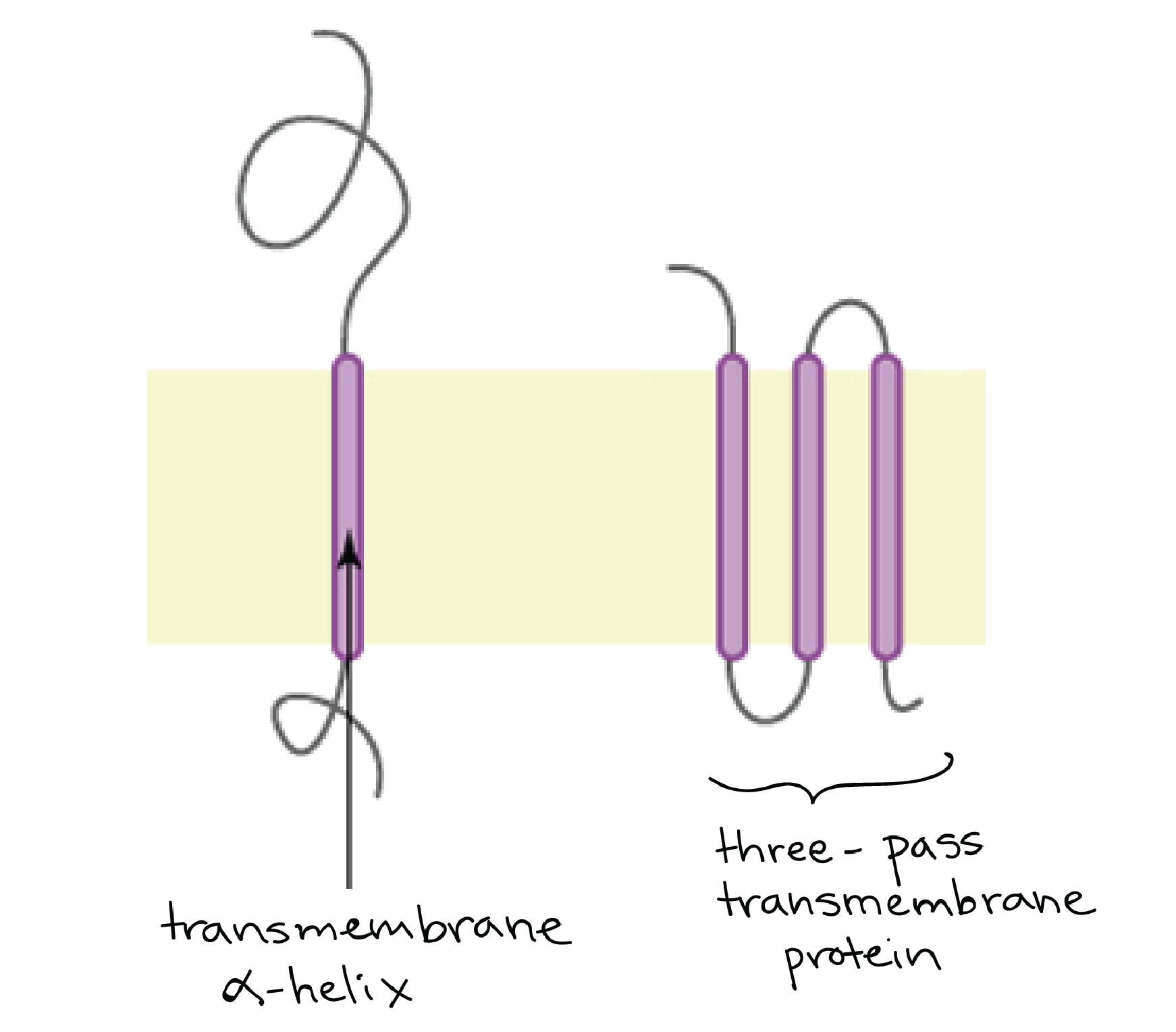
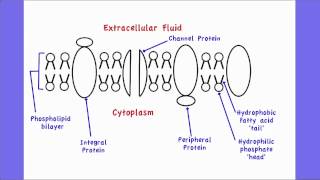
Question: What Is The Structure Of Membrane Proteins Integral membrane proteins, also called intrinsic proteins, have one or more segments that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. Most integral proteins contain residues with hydrophobic side chains that interact with fatty acyl groups of the membrane phospholipids, thus anchoring the protein to the membrane.
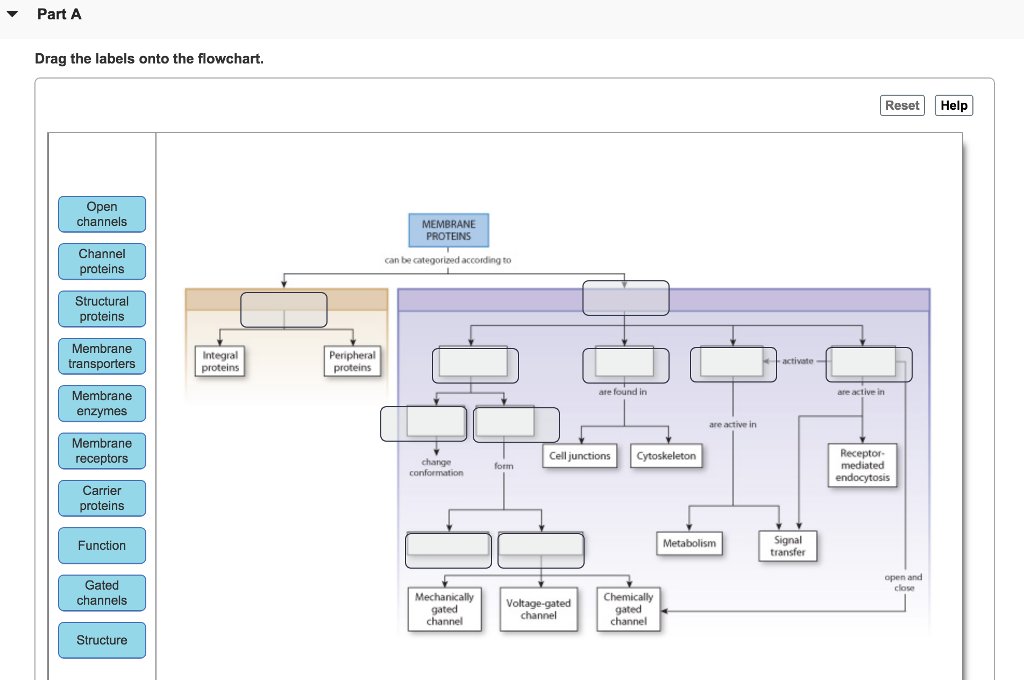
Label the structure and functions of membrane proteins
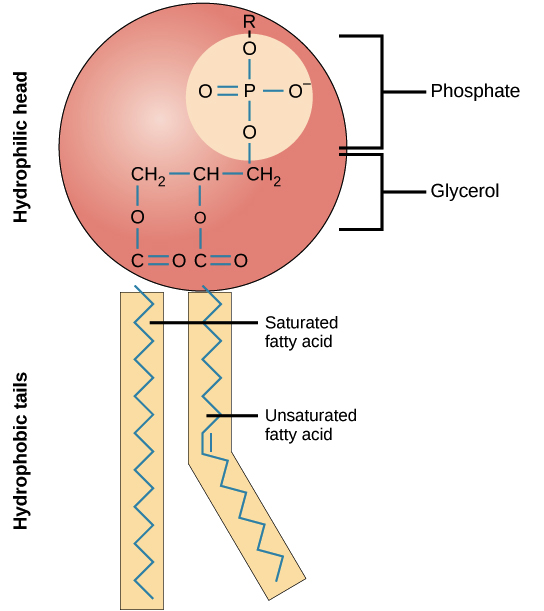
PDF Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function - WOU Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membrane Proteins: 1) Transport Proteins: • Regulate movement of hydrophilic molecules through membrane A) Channel Proteins (e.g. Na+ channels) B) Carrier Proteins (e.g. glucose transporter) 2) Receptor Proteins: • Trigger cell activity when molecule from outside environment binds to protein Learn About Membrane Structure And Functions | Chegg.com Body Membranes Structure and Function: Membranes protect the organ by covering them and do not allow unwanted substances inside or outside the organ. They are thin layers of epithelial tissue found below the connective tissues. Cutaneous membrane, serous membrane, mucous membranes, and synovial membranes are the four types of membranes. Structure of the Plasma Membrane - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
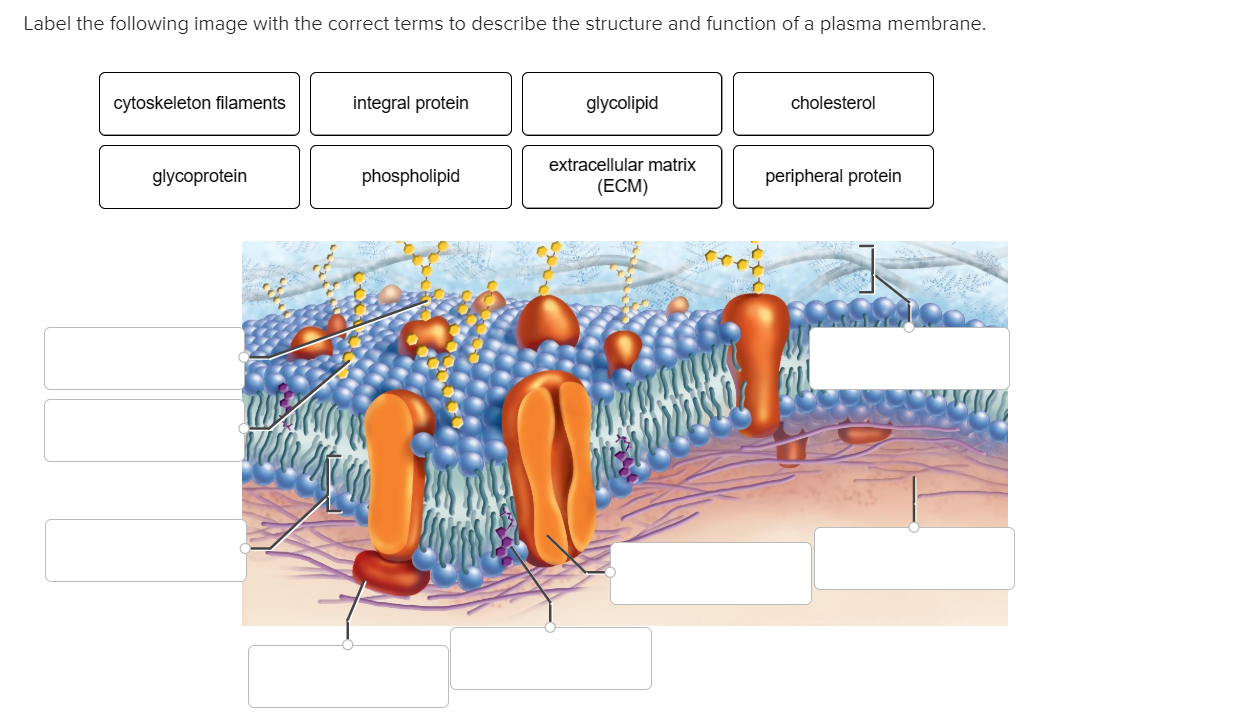
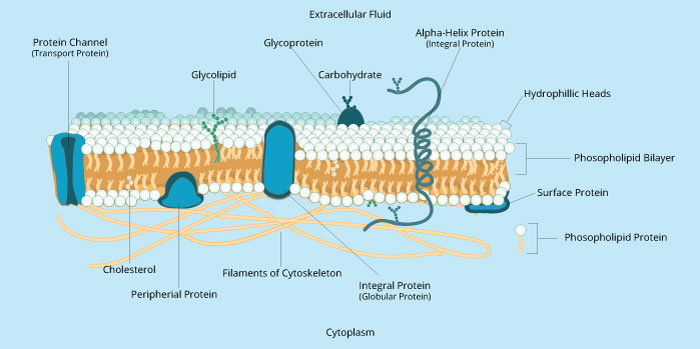
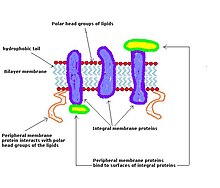
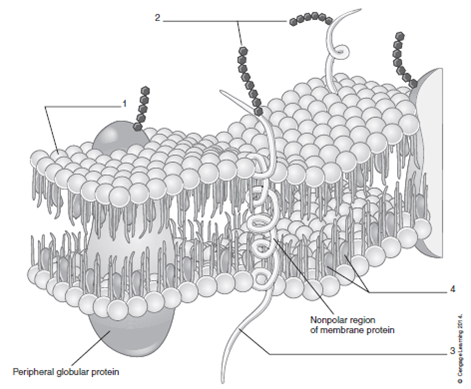
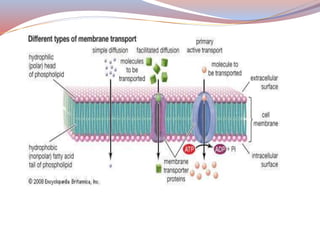
Label the structure and functions of membrane proteins. Solved Label the following image with the correct terms to - Chegg Question: Label the following image with the correct terms to describe the structure and function of a plasma membrane. cytoskeleton filaments integral protein glycolipid cholesterol glycoprotein phospholipid extracellular matrix (ECM) peripheral protein This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Structure & function of membrane proteins Flashcards | Quizlet Match. Gravity. Properties of membrane-spanning proteins (integral) Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 1) span the membrane more than one time; most alpha helix but sometimes beta. 2) structure often predicted by primary structure. 3) various functions. Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy Integral membrane proteins are, as their name suggests, integrated into the membrane: they have at least one hydrophobic region that anchors them to the hydrophobic core of the phospholipid bilayer. Some stick only partway into the membrane, while others stretch from one side of the membrane to the other and are exposed on either side. Plasma Membrane Function, Structure & Diagram - Study.com Proteins serve many important functions in the plasma membrane. Proteins that span the plasma membrane are called integral proteins. These proteins can be structural, helping to hold the shape of...
Membrane Protein Characterization and Structural Determination Structural and functional characterization of membrane proteins starts with extracting the protein from its native membrane environment using detergents. But finding the detergent that both solubilizes and preserves stability is difficult. This study applied label-free nanoDSF to rapidly screen 94 detergents by looking at the thermal stability ... Cell membrane - definition, structure, function, and biology The cell membrane is a thin biological membrane that separates the interior of cells from the outside space and protects the cells from the surrounding environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) with many kinds of proteins inserted. These proteins control the movement of molecules such as water, ions ... Membrane Structure and Function Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Membrane Structure and Function. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. ... interact with membrane proteins by charge; you have to affect charge/H bond in order to isolate them ... the idea that you can label a surface protein with a fluorescent tag, blast it with laser, and see if the ... 6 Important Types of Membrane Proteins (With Diagram) Some of the most important types of membrane proteins are as follows: 1. Peripheral (Extrinsic) Proteins 2. Integral (Intrinsic) Proteins 3. Asymmetric Distribution of Membrane Proteins 4. Mobility of Membrane Proteins 5. Enzymatic Properties of Membrane Proteins 6. Isolation and Characterization of Membrane Proteins. 1.
Structure and Function of Membrane Proteins: Proceedings of the ... Structure and Function of Membrane Proteins documents the proceedings of the International Symposium on Structure and Function of Membrane Proteins held in Selva di Fasano on May 23-26, 1983. This compilation makes it possible to obtain more information on the structure of membrane proteins, determining the structure in order to understand the function, and mechanism of action that is only ... Membrane Proteins: Functions, Types & Structure - Study.com Sep 17, 2021 · The structure of membrane proteins often determines their function. This, in turn, is the way we classify the type of membrane protein. In general, integral proteins are embedded within the... What Are the Functions of Membrane Proteins? - Reference.com The functions of a membrane protein include cell cohesion, relaying signals between the inside and outside of a cell and transporting proteins across the membrane. A membrane protein is a protein that is attached to a cell and interacts with biological membranes. Each type of membrane protein has a different function. Membrane Protein Structure, Function, and Dynamics: a Perspective from ... Membrane proteins mediate processes that are fundamental for the flourishing of biological cells. Membrane-embedded transporters move ions and larger solutes across membranes; receptors mediate communication between the cell and its environment and membrane-embedded enzymes catalyze chemical reactions.
Structure and Function of Membrane Proteins | ScienceDirect Tertiary structure and molecular shape of membrane proteins and structure-function relationship in membrane proteins are also examined. This book is a good source of information for students and individuals conducting research on biochemistry, specifically on membrane proteins.
Membrane Of Cell The Label Structure The Chegg The structure of the cell membrane is described by the fluid mosaic model which states that the cell membrane is a fluid-structure made up of a lipid bilayer along with 42-44 and pg Nucleolus 14 Plant cells are eukaryotic cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae The cell membrane is made out of two layers ...
Membrane Proteins - Microbe Notes Biological membranes consist of a continuous double layer of lipid molecules in which membrane proteins are embedded.; Although the lipid bilayer provides the basic structure of biological membranes, the membrane proteins perform most of the membrane's specific tasks and therefore give each type of cell membrane its characteristic functional properties.
Membrane Protein Structure and Function Characterization In this present volume, different approaches are detailed to produce membrane proteins, purify them, study their function, determine their structure, and model them in membrane. Since every membrane protein behaves mostly in a unique way /fashion, knowledge of guidelines and tricks may help to increase chances to express, purify and ...
Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo Oct 07, 2019 · Portions of these transmembrane proteins are exposed on both sides of the membrane. Cell membrane proteins have a number of different functions. Structural proteins help to give the cell support and shape. Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules. Transport proteins, such as globular proteins, transport molecules across cell membranes through facilitated diffusion.
1.3: Membrane Structure Flashcards | Quizlet Understanding: Membrane proteins are diverse in terms of structure, position in the membranes and function. 1. Receptor proteins receive extracellular signals. 2. Transport proteins move ions and molecules across the bilayer. 3. Enzymes catalyze reactions. 4. Adhesion proteins anchor the cell to other cells. 5.
Membrane protein structure and function - PubMed Membrane Proteins / genetics Membrane Proteins / metabolism* Protein Structure, Secondary
PDF Membrane Structure and Function - Phoenix College Functions of the Cell Membrane • Contains the cell • Regulates the traffic of molecules and substances in and out of the cell (semi- permeable membrane) Traffic of Substances Across the Plasma Membrane • Selective • Bidirectional • Depending Upon Differences of Concentration Inside and Outside of the Cell
Membrane structure and function - PubMed Membrane structure and function An understanding of the biochemical basis of membrane function is an important goal of present day biology. In this paper, a biochemical approach to the problem of the specific transport of sugars across the membrane of Escherichia coli is discussed. A new biochemical model for lactose transport sys …
Cell Membrane Structure and Function - Biology Wise Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell (in animals). In plant cells, the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
Structure of the Membrane | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning Integral proteins are embedded in the plasma membrane and may span all or part of the membrane. Integral proteins may serve as channels or pumps to move materials into or out of the cell. Peripheral proteins are found on the exterior or interior surfaces of membranes, attached either to integral proteins or to phospholipid molecules.
Chap 5: Membrane Structure and Function Flashcards - Quizlet Describe at least three of the six functions of plasma membrane proteins. -transporter -enzyme -cell-surface receptor -cell-surface identity marker -cell-to-cell adhesion -attachment to the cytoskeleton functions of plasma membrane integral proteins (img) transporter (def) a function of plasma membrane proteins
Membrane Proteins - Biology Reader Membrane proteins are the binding proteins that mediate the conduction of ions or molecules into and out of the cell membrane. Integral, peripheral and lipid-anchored are the three typical membrane proteins. The membrane protein is the principal constituent of the cell membrane that contributes to the plasma membrane structure.
Structure of the Plasma Membrane - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
Learn About Membrane Structure And Functions | Chegg.com Body Membranes Structure and Function: Membranes protect the organ by covering them and do not allow unwanted substances inside or outside the organ. They are thin layers of epithelial tissue found below the connective tissues. Cutaneous membrane, serous membrane, mucous membranes, and synovial membranes are the four types of membranes.
PDF Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function - WOU Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membrane Proteins: 1) Transport Proteins: • Regulate movement of hydrophilic molecules through membrane A) Channel Proteins (e.g. Na+ channels) B) Carrier Proteins (e.g. glucose transporter) 2) Receptor Proteins: • Trigger cell activity when molecule from outside environment binds to protein











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)



Post a Comment for "39 label the structure and functions of membrane proteins"