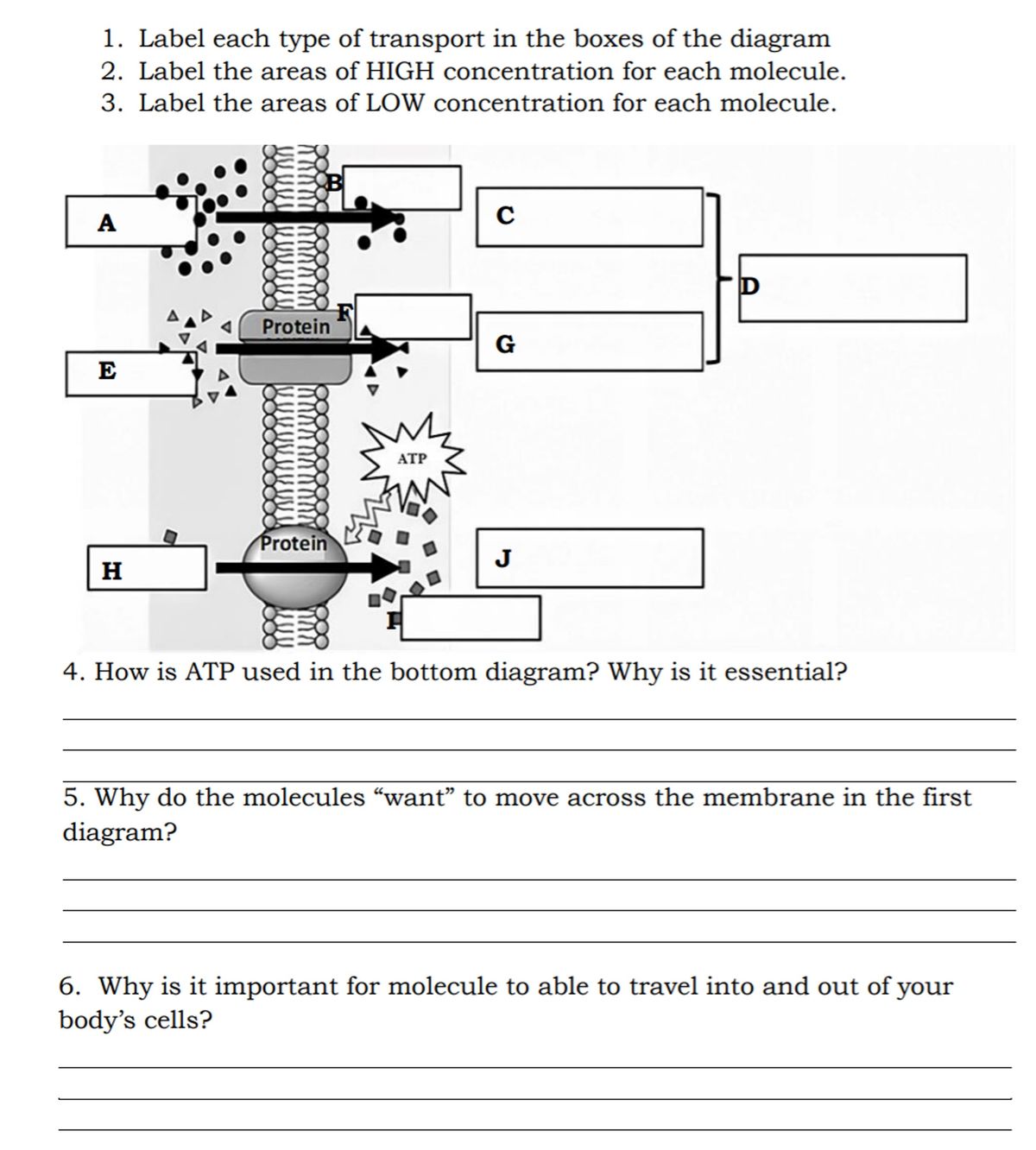
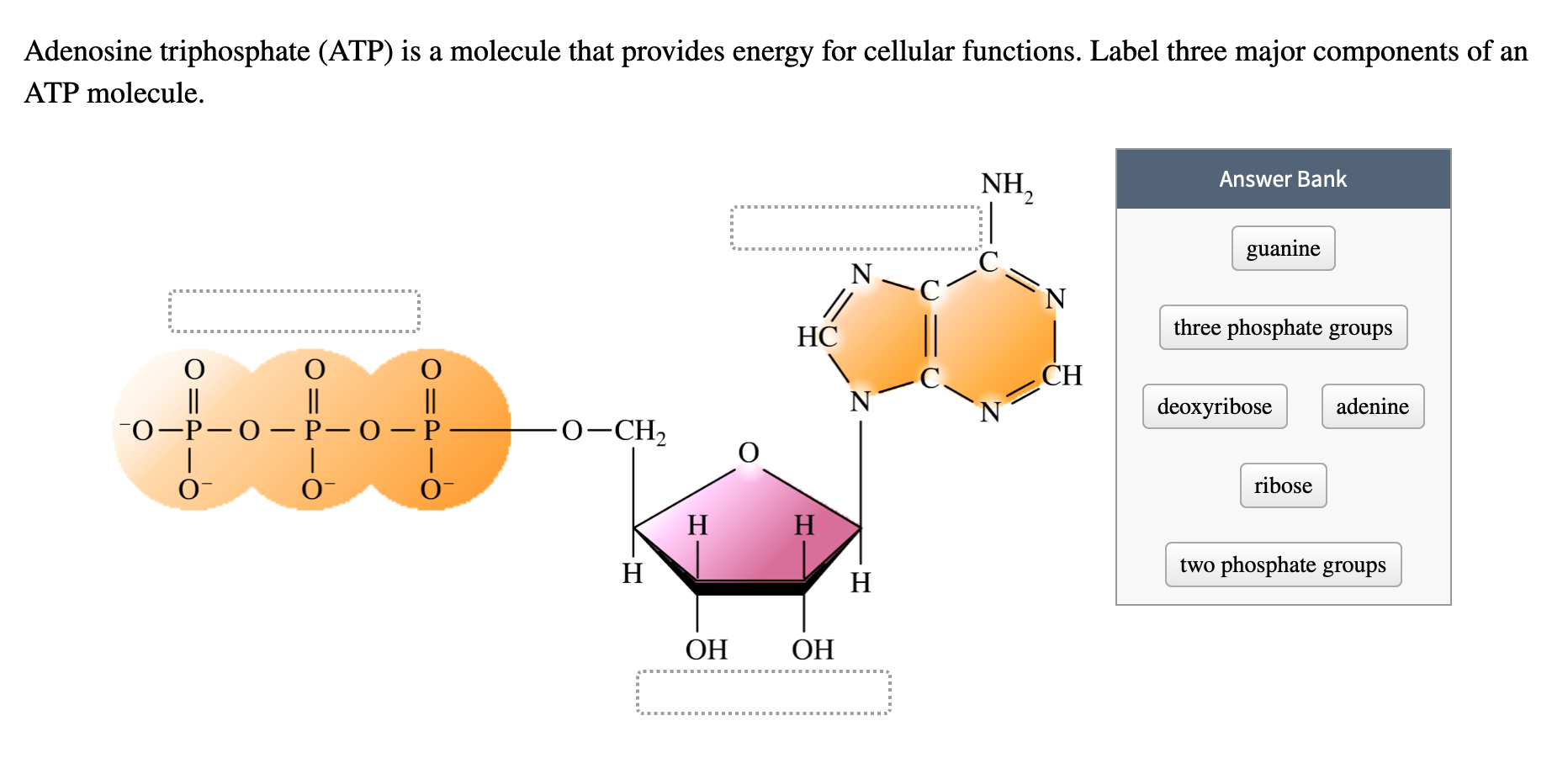
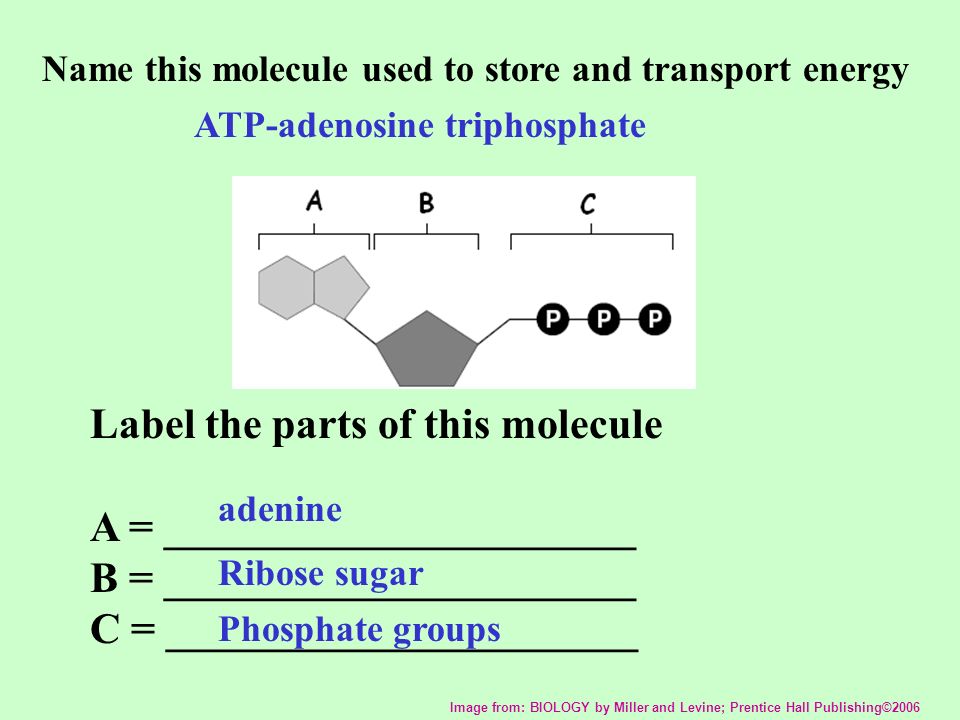
38 label the parts of the atp molecule
Solved Part 2 (1 pt) See Hint Within the image of ATP, label - Chegg Question 1 First portion is Phosphate groups -Here three Phosphate groups are linked to each other. Second middle portion is ribose sugar , its 2'Carbon have -OH group (Contains Oxygen atom), and it is a 5-C sugar. Third last portion is Adenine - It … View the full answer SKELETAL MUSCLE ORGANIZATION - Brigham Young … It is the ATP that provides the energy for muscle contraction. Each of the myosin heads is associated with two myosin light chains that play a role in regulating the actions of the myosin heads, but the exact mechanism is not fully understood. The three dimensional arrangement of the myosin heads is very important. Imagine that you were looking at a thick filament from the …
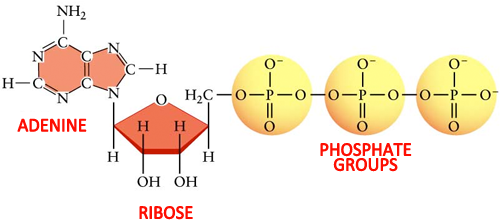
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Explanation: Adenosine triphosphate, commonly known as ATP, is the energy carrier molecule in living cells. ATP is structurally composed of Adenine molecule (a nitrogenous base), Ribose (pentose sugar) and three phosphate groups. Energy in ATP is stored in the bonds that hold the phosphate groups together.

Label the parts of the atp molecule
Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive It is on these cristae that food (sugar) is combined with oxygen to produce ATP - the primary energy source for the cell. Vacuole: A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that plays roles in intracellular digestion and the release of cellular waste products. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small. Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play several roles: storing nutrients … ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Updated on May 09, 2019. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed. Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP molecule ... ATP or adenosine triphosphate or Adenine- ribose-phosphate-phosphate-phosphate. The bonds joining the additional phosphate groups o the nucleotides are called high energy or energy-rich bonds. Adenine- It is a nitrogenous base of 9 membered double ring purine.
Label the parts of the atp molecule. PharmaCircle This website uses cookies to help provide you with the best possible online experience. Please read our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy for information about ... Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems.Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg 2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source Facilitated Diffusion: Definition, Types, and Examples - Research … 18.09.2021 · Although majority of facilitated diffusion does not suffice the need of ATP, however in few cases it does require ATP. Facilitated diffusion take place due to the exactitude between the carriers and the solute. In facilitated diffusion molecules can progress in both the direction i.e., towards or against the concentration gradient. Kinetic ...
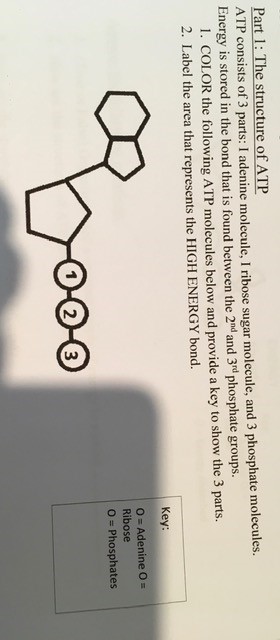
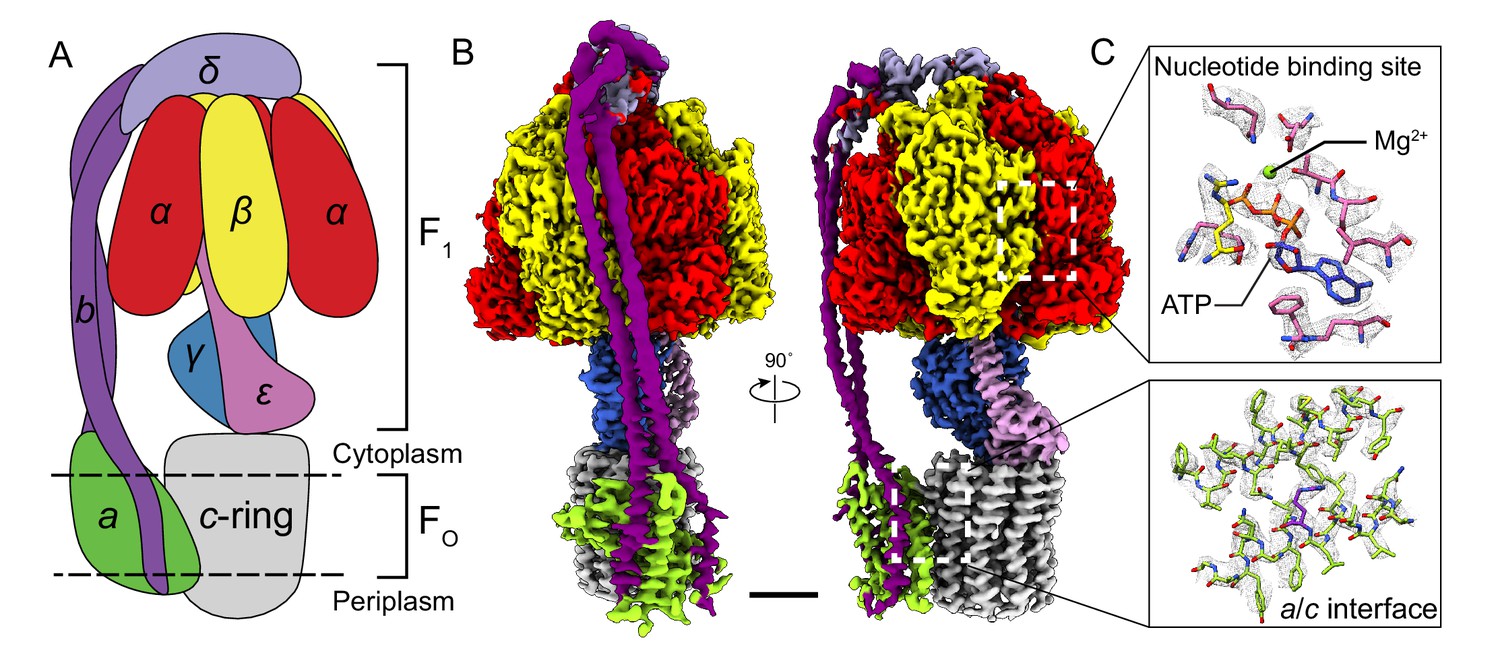
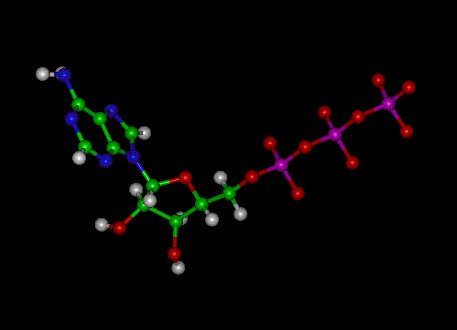
ATP.docx - ATP—The Free Energy Carrier How does the ATP molecule ... View ATP.docx from BIO 101 at Issaquah High School. ATP—The Free Energy Carrier How does the ATP molecule capture, store, and release energy? Why? A sporting goods store might accept a $100 bill for Answered: 3 (ii) In the Haber process for the… | bartleby Science Chemistry Q&A Library 3 (ii) In the Haber process for the production of ammonia the following reaction occurs: 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) N2 (8) + AH is negative If the equilibrium concentrations for all the reactants and products at 600°C are: [N₂] = 0.40 mol/dm³, [H₂] = 1.20 mol/dm³ and [NH3] = 0.20 mol/dm³ what is the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, Ke? Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The ATP molecule is composed of three components. These phosphates are the key to the activity of ATP. ATP consists of a base, in this case adenine (red), a ribose (magenta) and a phosphate chain (blue). All living things, plants and animals, require a continual supply of energy in order to function. Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine ), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate . Contents 1 Structure 1.1 Binding of metal cations to ATP 2 Chemical properties 3 Reactive aspects 4 Production from AMP and ADP
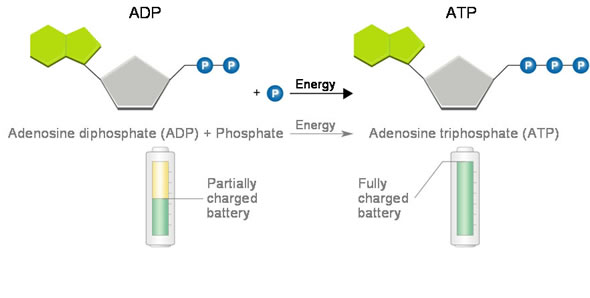
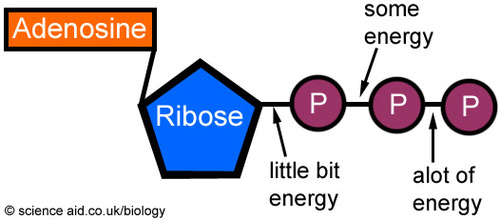
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) … View the full answer DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Explanation: Adenosine triphosphate, commonly known as ATP, is the energy carrier molecule in living cells. ATP is structurally composed of Adenine molecule (a nitrogenous base), Ribose (pentose sugar) and three phosphate groups. Energy in ATP is stored in the bonds that hold the phosphate groups together. Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency ...
Biology 1 CP Study Guide: ATP and Phototsynthesis - Quizlet What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? Adenine, Ribose, Phosphate Which parts of an ATP molecule combine to form Adenosine? Adenine and Ribose What does ATP stand for? Adenosine TriPhosphate What does ADP stand for? Adenosine DiPhosphate What is the main way cells get energy from ATP? From the breakdown of food molecules
ATP Diagram | Quizlet Terms in this set (9) ATP (name) adenosine triphosphate. ADP (name) adenosine diphosphate. ATP (function) a high energy molecule that transfers energy in cells. ADP (function) a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP.
ATP_worksheet.docx - Name:_ Date:_ Block:_ Chemical Energy... Label the following structures in the diagram below as ATP or ADP. a. _____ b. _____ ATP COLORING : the 3 p are blue ribose are red and adeinine yellow Adenine = Blue Tri-Phosphate = Red Ribose = Yellow. ... Stored Energy, parts of an ATP molecule. Share this link with a friend:
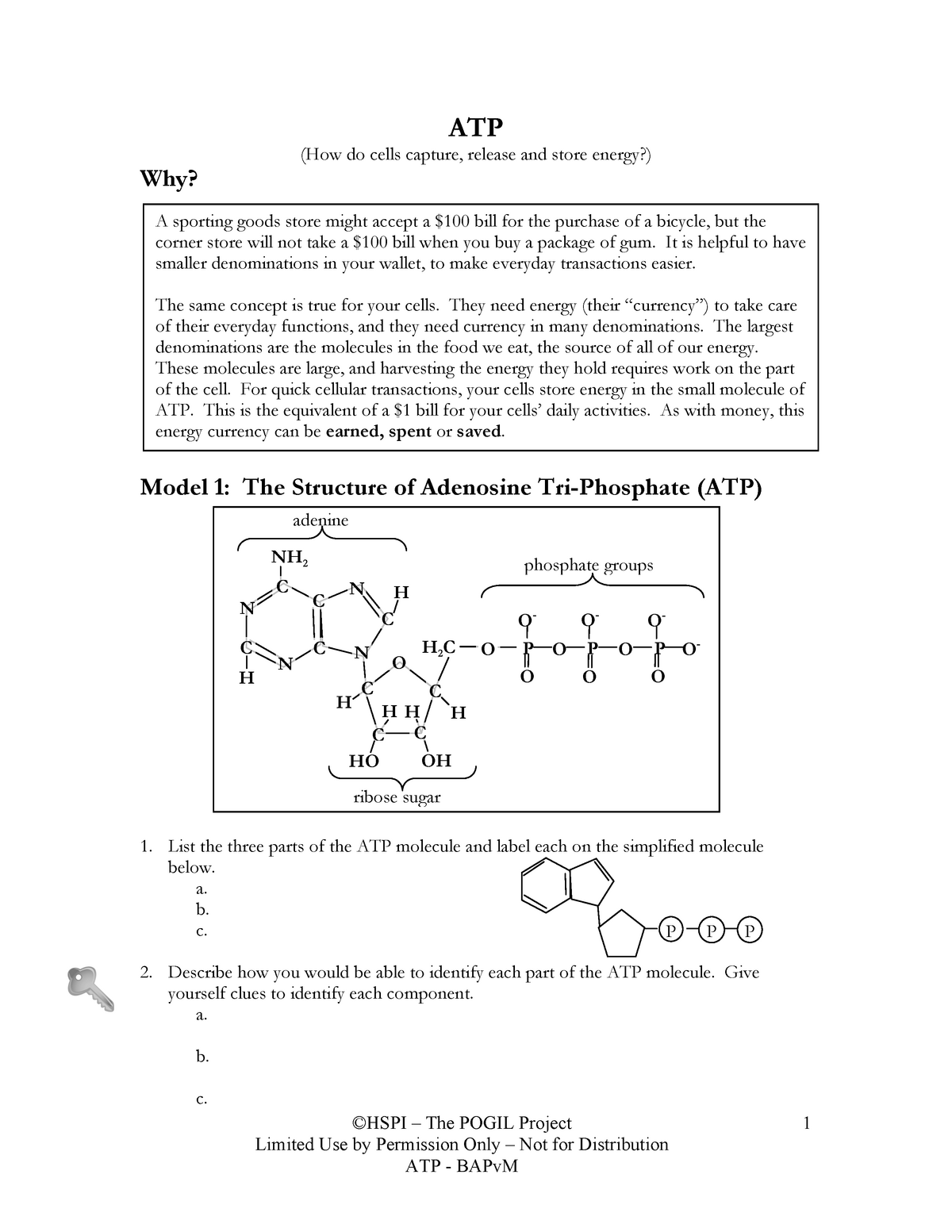
PDF ATP - Loudoun County Public Schools List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c. A sporting goods store might accept a $100 bill for the purchase of a bicycle, but the
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace [34] Mutations have been found throughout the ATRX protein, with over 90% of them being located in the zinc finger and helicase domains. They also play an important role in sensing viral RNAs. Label each part of the atp molecule above in the spaces provided. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. How does atp differ from adp.
ATP/ADP | Photosynthesis Quiz - Quizizz answer choices. The breaking of the bond between the 5-carbon sugar and the 1st phosphate group. The addition of a phosphate group. The removal of a phosphate group. The addition of glucose. Question 10. 30 seconds. Q. Where is the energy stored in ATP molecules.
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
ATP-Student - ATP - ©HSPI - The POGIL Project Limited Use by Permission ... ATP (How do cells capture, release and store energy?) Why? Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c.
Energy and Life: The Transformation of Energy in Living Organisms Label each test tube 1-4. In test tube one add nothing, in test tube 2 put one sprig of the aquatic plant, in test tube 3 place one snail, and in test tube 4 place both a snail and an aquatic ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases.
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ATP is made up of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate molecules. ATP contains one adenine (blue), one sugar (pink), and three phosphate groups. ATP Meaning ATP follows the same rules of...
ATP Overview & Uses | What Does ATP Stand For? - Study.com ATP definition: ATP is a high-energy molecule that can be found in all types of cells, including plant cells, muscle cells, nerve cells, and more. ATP is part of the larger macromolecule category ...
What are the three parts of the ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
Home | Cedar Park Church Kids. We know your kids are important to you; they’re a big deal! They are not just hope for the future, but they are important today. We feel the same way; kids are not just the future of the church - they are the church!
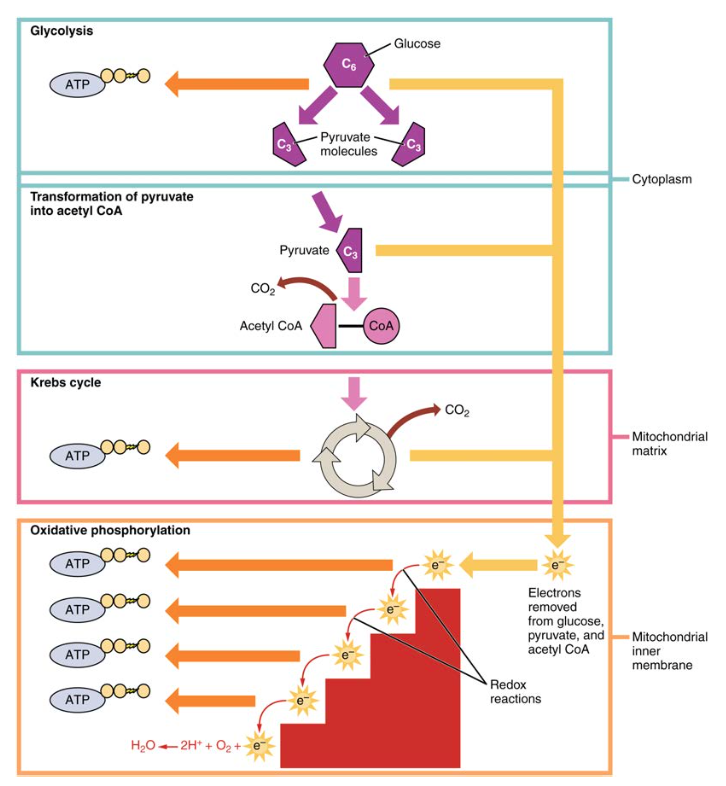
ATP Production - The Mitochondria The production of ATP is called the process of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy in the form of glucose. Here are three steps before the ATP is created in the mitochondria. The first step is called Glycolysis. Then there is The Krebs Cycle and last there is the Electron Transport Chain before ATP is ...
adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ...
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules ATP consists of adenosine - composed of an adenine ring and a ribose sugar - and three phosphate groups (triphosphate). The phosphoryl groups, starting with the group closest to the ribose, are referred to as the alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) phosphates. Consequently, it is closely related to the adenine nucleotide, a monomer of RNA.
Krebs / citric acid cycle (video) | Khan Academy So we already know that if we start off with a glucose molecule, which is a 6-carbon molecule, that this essentially gets split in half by glycolysis and we end up 2 pyruvic acids or two pyruvate molecules. So glycolysis literally splits this in half. It lyses the glucose. We end up with two pyruvates or pyruvic acids. ruby And these are 3 ...
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group.
Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP molecule ... ATP or adenosine triphosphate or Adenine- ribose-phosphate-phosphate-phosphate. The bonds joining the additional phosphate groups o the nucleotides are called high energy or energy-rich bonds. Adenine- It is a nitrogenous base of 9 membered double ring purine.
ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Updated on May 09, 2019. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed.
Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive It is on these cristae that food (sugar) is combined with oxygen to produce ATP - the primary energy source for the cell. Vacuole: A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that plays roles in intracellular digestion and the release of cellular waste products. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small. Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play several roles: storing nutrients …

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)














Post a Comment for "38 label the parts of the atp molecule"