44 phospholipid bilayer diagram
Phospholipid - Wikipedia Phospholipid bilayers are the main structural component of the cell membranes. In biological membranes, the phospholipids often occur with other molecules (e.g., proteins, glycolipids, sterols) in a bilayer such as a cell membrane. Effect of cholesterol on the structure of a phospholipid bilayer phospholipid membranes. To obtain a detailed understanding of the lipid-cholesterol interactions, we have developed a mesoscopic water-lipid-cholesterol model. In this model, we take into account the hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions and the structure of the molecules. We compute the phase diagram of dimyristoylphosphati-
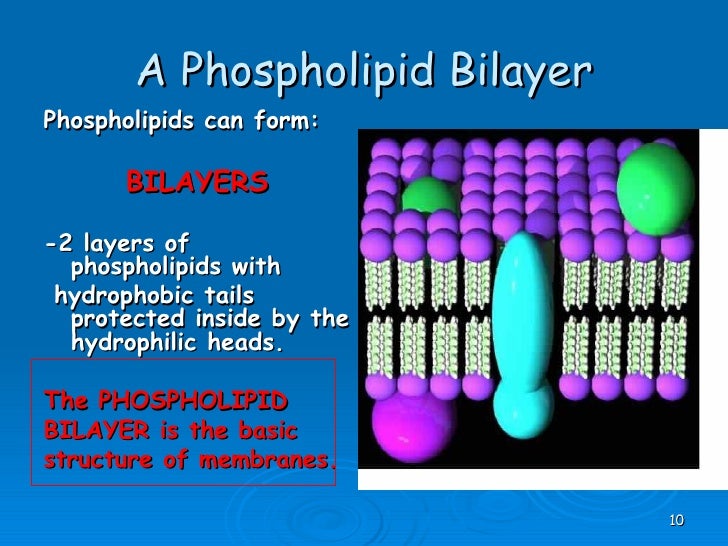
Phospholipids - Structure, Types, Properties and Function The phospholipid bilayer is made up of two adjacent phospholipid sheets that are arranged tail to tail. The hydrophobic tails interact with one another to generate the membrane's interior. The fluid inside and outside the cell is contacted by the polar heads.

Phospholipid bilayer diagram
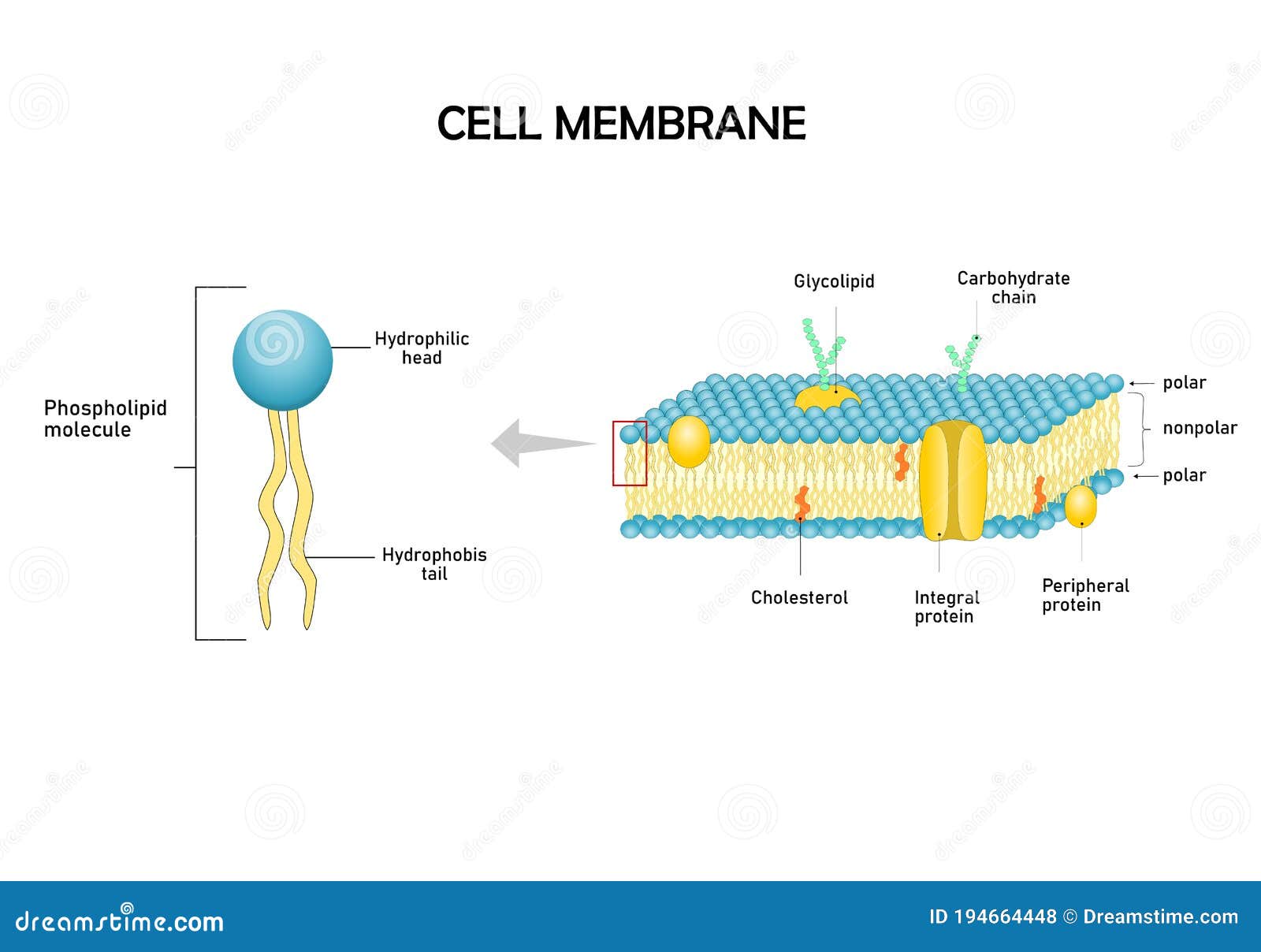
Structure of the Plasma Membrane - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf First, the structure of phospholipidsis responsible for the basic function of membranes as barriers between two aqueous compartments. Because the interior of the phospholipid bilayeris occupied by hydrophobicfatty acid chains, the membrane is impermeable to water-soluble molecules, including ions and most biological molecules. Label the Phospholipid Bilayer Diagram | Quizlet phospholipid composed of a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head hydrophilic heads Negative charge so they attract to water hydrophobic tails Fatty acids are nonpolar and hydrophobic cholesterol maintain fluidity of the membrane and prevent non polar fatty acid tails from sticking together even in cold temperatures peripheral protein Phospholipid Bilayer | Introduction, Structure and Functions Phospholipid Diagram Phospholipid Structure A Phospholipid molecule is comprised of two Fatty Acid tails and Phosphate Group which make its Head. Fatty acids are chemically composed of long chains of Hydrogen and Carbon atoms. While Phosphate groups comprised of a Phosphorus molecule. Four oxygen molecules attached to Phosphate group.
Phospholipid bilayer diagram. Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function | Biology Dictionary This figure depicts the lipid bilayer and the structure of a phospholipid: Functions of Phospholipids As membrane components, phospholipids are selectively permeable (also called semi-permeable), meaning that only certain molecules can pass through them to enter or exit the cell. Phospholipid Bi-Layer Diagram - SmartDraw Phospholipid Bi-Layer Diagram Create Biology Diagram examples like this template called Phospholipid Bi-Layer Diagram that you can easily edit and customize in minutes. 7/20 EXAMPLES EDIT THIS EXAMPLE Text in this Example: Na- Phospholipid Bi-layer (Potasium Ion Channel example) Cytoplasm Sodium Ion Channel Potassium Ion K+ Phospholipid CH CH2 CH3 Phospholipid Bilayer Diagram | Quizlet -anchors RBC membrane cytoskeleton to lipid bilayer -carries antigens peripheral protein -spectrins -provide RBC with deformability -binds to actin and ankyrin to form cytoskeleton phosphate heads -hydrophilic -polar lipid tails -hydrophobic -nonpolar antigen identifies the cell as "self" cholesterol -provides stiffness to the membrane Phospholipid Structure & Function | What is a Phospholipid? The phospholipid is shaped like a thumbtack with two tails protruding from the head. The head is the phosphate group, and the tails are the two fatty acids. The heads are closer to the inner and...
Solved A phospholipid bilayer is depicted in the diagram - Chegg A phospholipid bilayer is depicted in the diagram below. Phospholipids are molecules that have two regions, the head and the tail, with distinct chemical properties. Classify the following descriptions as characteristics of the heads or tails of phospholipids. Question: A phospholipid bilayer is depicted in the diagram below. Phospholipid Bilayer Function & Structure | What Does the Phospholipid ... First, the phospholipid bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipids. The chemical structure of the phospholipids and the orientation of the bilayer prevent large or hydrophilic molecules... Phospholipid Bilayer Structure - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The phospholipid bilayer structure illustrates the combined effects of hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions, which are two kinds of most important noncovalent interactions. In this structure the nonpolar fatty acid chains of the phospholipid are sequestered together away from contact with water, thereby maximizing hydrophobic interactions. Phospholipid Bilayer | BioNinja • Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules Structure of Phospholipids: Consist of a polar head (hydrophilic) composed of a glycerol and a phosphate molecule Consist of two non-polar tails (hydrophobic) composed of fatty acid (hydrocarbon) chains
Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function, Examples - Science Terms Phospholipid Definition. A phospholipid is an amphiphilic molecule consisting of a polar head region, a unit of glycerol, and two or more non-polar fatty acid tails, typically found in a cell membrane. A bilayer of phospholipid molecules forms a plasma membrane.. When the phospholipid molecules are joined by other lipids and integral proteins, the surface can function as a cellular membrane. Membranes Interactive Tutorial 1: The Phospholipid Bilayer 1. Phospholipids and the phospholipid bilayer The key molecule in the membrane is a phospholipid. Like triglycerides (fats and oils), phospholipids are built around a molecule of glycerol, a 3-carbon alcohol, (shown in pink at number 2 in the diagram). Attached to the glycerol on one side are two fatty acids (shown in yellow at number 3). Phospholipids | Introduction to Chemistry | | Course Hero The cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. The fatty acid tails of phospholipids face inside, away from water, whereas the phosphate heads face the outward aqueous side. Since the heads face outward, one layer is exposed to the interior of the cell and one layer is exposed to the exterior. Phospholipid Bilayer - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Phospholipid bilayer Nanodiscs (Bayburt and Sligar, 2009; ... The BLM system is a quasi-two-dimensional flexible structure that undergoes continuously a variety of conformational and dynamic transitions [41-44]. Furthermore, the artificial and natural BLMs are not insulating systems, but permeable for water and electrolytes that diffuse across ...
This is an image of the phospholipid bilayer, what is the name of the ... Weegy: This is an image of the phospholipid bilayer. Based on what you know about the structure of the phospholipid bilayer, The side labeled 2 in the image of the phospholipid bilayer is the "hydrophobic side". [ The phospholipid "tails" are hydrophobic. ] Weegy: High intensity of light, high levels of carbon dioxide, moderate temperature ...
What is the Phospholipid Bilayer? (with pictures) Purpose Cholesterol helps stabilize phospholipid bilayer, but too much cholesterol can be dangerous for arteries involved in blood flow. One of the main purposes of the phospholipid bilayer are to provide structure to a cell, which it does because of the natural arrangement of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends of the phospholipids, and with the stabilizing cholesterol and sterols. Its other ...
Phospholipid structure (video) | Cells | Khan Academy Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this. It has that polar phosphate head group, and it has two fatty acid chains. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. But what does that really mean? What dose is picture actually look like down to a molecule? Well, let's talk about the first one, the fatty acid.
PDF Figure 7.5 Phospholipid bilayer Fig. 7-2 Phospholipid bilayer Membrane Structure: The Fluid Mosaic Model • Proteins embedded and floating in a sea of phospholipids 1972 Singer & Nicholson Figure 7.3 Protein and Lipid raft A B hydrophobic hydrophilic 2 • Membrane proteins and lipids are synthesized in the ER and Golgi apparatus ER Figure 7.10
Phospholipid Bilayer | Lipid Bilayer | Structures & Functions Phospholipid Bilayer: All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes, and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic Model. According to this model, which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s, plasma membranes are composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates that are arranged in a " mosaic-like " manner.
What is the phospholipid bilayer and what determines its fluidity? This membrane is often referred to as the phospholipid bilayer. As you can probably tell from the name, a phospholipid bilayer is made up of two layers of lipids. The fluidity of this membrane must be maintained within a certain range for the cell to function properly. There are a number of factors that help influence membrane fluidity.
Cell Membrane Phospholipid Bilayer Structure Monday, January 25th 2021. | Diagram Cell Membrane Phospholipid Bilayer. As shown in Figure below, each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. There are much easier solutions to stop pain from taking over your body.
Bilayer Cell Membrane - Definition, Composition, Functions & Structure ... The bilayer cell membrane is a membranous structure, which consists of two phospholipid layers. Thus, a cell membrane also refers to a phospholipid bilayer membrane composed of many phospholipid molecules.. A structure of a phospholipid molecule consists of a hydrophilic head, a phosphate molecule, a glycerol molecule and two hydrophobic fatty acid tail.
The Cell Membrane - Structure - TeachMePhysiology Phospholipids. The membrane bilayer contains many kinds of phospholipid molecules, with different sized head and tail molecules.. These consist of a head molecule, a phosphate molecule, a glycerol and two fatty acid chains. Head group- This is a polar group e.g. a sugar or choline - meaning that the head end of the phospholipid is hydrophilic.; Tail of 2 fatty acid chains - normally ...


Post a Comment for "44 phospholipid bilayer diagram"